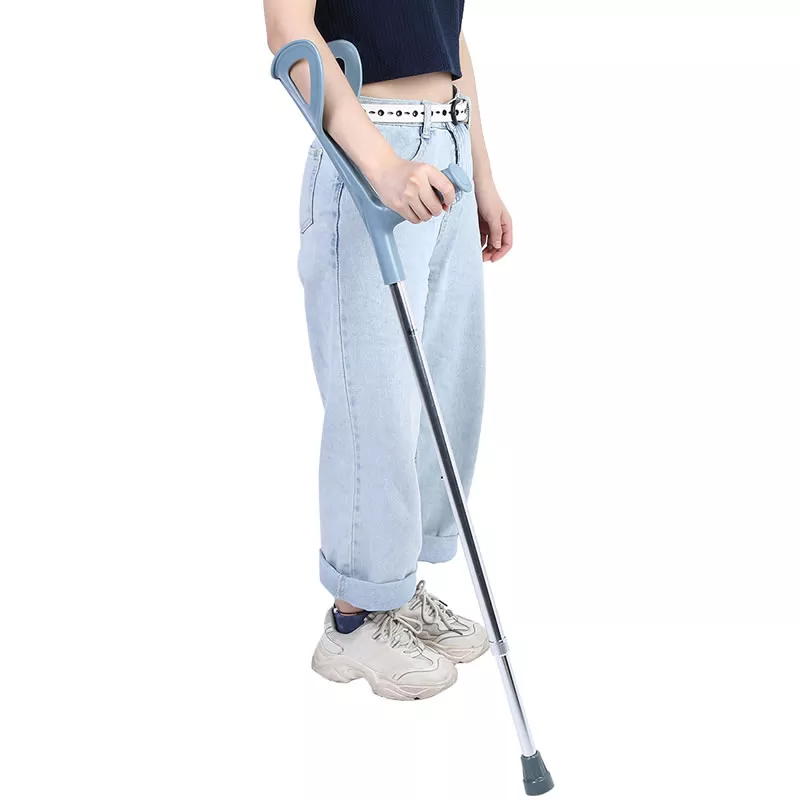
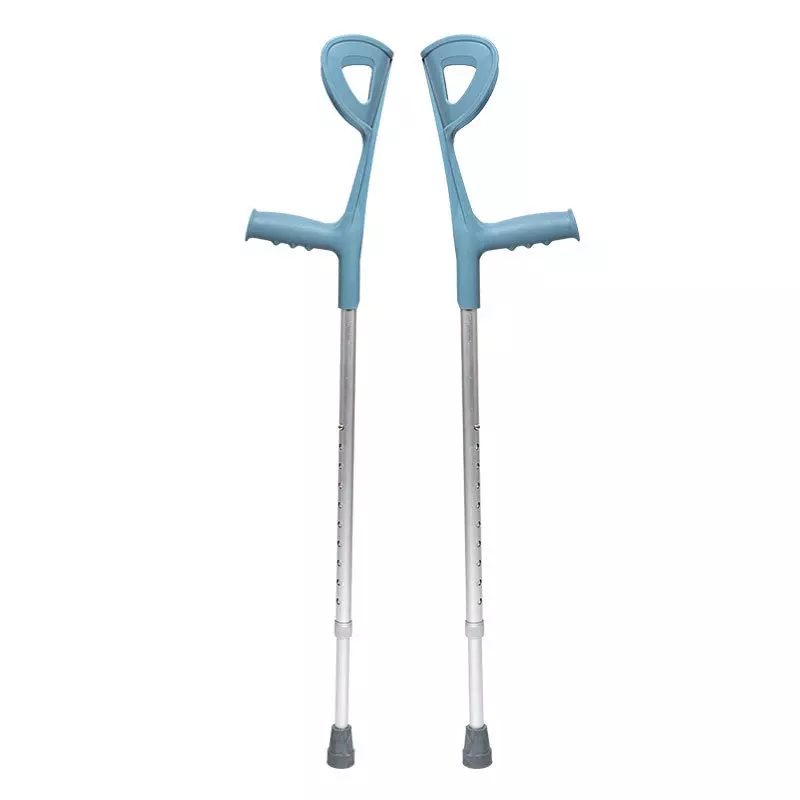
Forearm Elbow crutch
| ➢ | Seat Width (Upholstery): 18” |
| ➢ | Mainly used to accept greater load-bearing needs and stronger propulsive loads when walking. |
| ➢ | Suitable for: patients who need to support more body weight |
| ➢ | For example: spinal cord injury, pediatric paralysis, amputation, fracture, post-operative fracture |
| ➢ | patients |
| ➢ | The main stress point is the wrist joint. |
| ➢ | Made in aluminium |
| ➢ | Can come with push button mechanism. Forearm cuffs allow use of hands without disengaging |
| ➢ | the crutch. |
| ➢ | The crutches accommodate users from 5ft and support weight up to 350 lbs. |
What is Forearm Elbow Stick?
Forearm cane (Forearm Elbow Stick): also known as Lofstrand crutch, the position of the handle and the length of the strut can be adjusted, clamping the forearm arm sleeve is usually in the form of a folding leaf, there are two types of front and side openings. This crutch can be used singly or doubly, for poor grip, forearm weakness, but do not need to use the axillary cane people.
Advantages for light, beautiful, and with the crutch, the hand can still move freely; for example, when you need to use the hand to open the door, the hand can be detached from the handle to turn the door handle, without worrying about the cane off, the reason is that the arm sleeve still fixed the crutch on the forearm. The disadvantage of this crutch is that it is not as stable as the axillary crutch.
Forearm Cane Features
◾ Mainly used to accept greater load-bearing needs and stronger propulsive loads when walking.
◾ Suitable for: patients who need to support more body weight
For example: spinal cord injury, pediatric paralysis, amputation, fracture, post-operative fracture patients
◾ The main stress point is the wrist joint.
Crutches are medical devices designed to aid in ambulation, by transferring body weight from the legs to the torso and arms. They are mainly used to assist individuals with lower extremity injuries and/or neurological impairment. This activity describes the types of crutches, their indications, and contraindications and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in proper evaluation and training of patients needing ambulatory devices.